Model 2 the carbon cycle answer key – Delve into the intricacies of Model 2 of the carbon cycle, a powerful tool for understanding the Earth’s carbon dynamics. This comprehensive guide and answer key provides a clear and concise exploration of its assumptions, limitations, and applications, empowering you to unravel the complexities of this essential environmental process.
Model 2 of the carbon cycle offers a structured framework for analyzing the exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, and living organisms. By delving into its key features and components, we gain insights into the processes that shape our planet’s carbon balance and the potential impacts of human activities on this delicate equilibrium.
The Carbon Cycle: Processes and Interactions

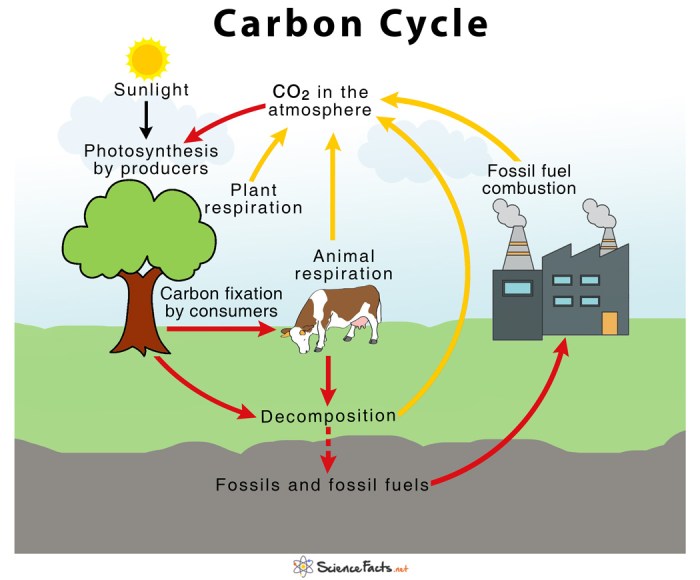
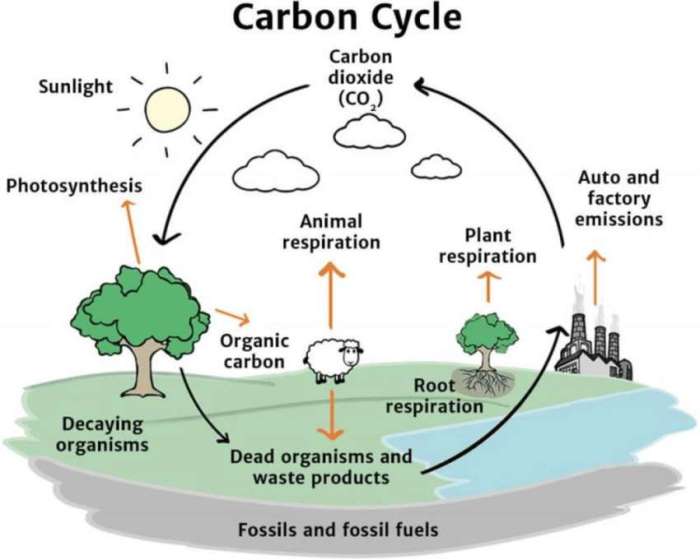
The carbon cycle is a fundamental process that involves the exchange of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. This complex system plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate and sustaining life on our planet.
Photosynthesis, a process performed by plants and certain microorganisms, converts carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into organic compounds, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. Conversely, respiration, a metabolic process occurring in all living organisms, releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
The ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide through various processes, including diffusion and the absorption of carbon dioxide by seawater. The ocean serves as a significant carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Living organisms play a vital role in carbon sequestration, the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Trees and other plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and store it in their biomass. Marine organisms, such as phytoplankton, also contribute to carbon sequestration by converting carbon dioxide into calcium carbonate, which sinks to the ocean floor.
Model 2 of the Carbon Cycle
Model 2 of the carbon cycle is a mathematical representation that simulates the exchange of carbon between different reservoirs on Earth. It provides a simplified framework for understanding the dynamics of the carbon cycle and predicting future carbon dioxide levels.
Model 2 assumes that the carbon cycle is a closed system, with no external inputs or outputs. It divides the carbon cycle into several compartments, including the atmosphere, ocean, land, and living organisms. Each compartment contains a specific amount of carbon, and carbon is exchanged between compartments through various processes.
Model 2 incorporates data on carbon fluxes, such as the rate of photosynthesis, respiration, and ocean-atmosphere exchange. It uses this data to calculate the amount of carbon in each compartment and to simulate the changes in carbon levels over time.
Key Features and Components of Model 2
- Divides the carbon cycle into several compartments, including the atmosphere, ocean, land, and living organisms.
- Assumes that the carbon cycle is a closed system, with no external inputs or outputs.
- Uses data on carbon fluxes to calculate the amount of carbon in each compartment and to simulate the changes in carbon levels over time.
- Provides a simplified framework for understanding the dynamics of the carbon cycle and predicting future carbon dioxide levels.
Applications and Uses of Model 2
Model 2 is a valuable tool for understanding the carbon cycle and predicting future carbon dioxide levels. It is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Predicting future carbon dioxide levels: Model 2 can be used to simulate the effects of different scenarios, such as changes in land use or fossil fuel emissions, on future carbon dioxide levels.
- Informing policy decisions related to climate change mitigation: Model 2 can help policymakers understand the potential impacts of different climate change mitigation strategies, such as reducing fossil fuel emissions or promoting reforestation.
- Carbon accounting and management: Model 2 can be used to track carbon emissions and removals, and to develop strategies for reducing carbon footprints.
Comparisons with Other Carbon Cycle Models
Model 2 is one of several carbon cycle models that have been developed. Other models include Model 1 and the Bern Carbon Cycle Model.
Model 1 is a simpler model than Model 2, and it does not include as many compartments or processes. Model 1 is often used for educational purposes or for quick simulations.
The Bern Carbon Cycle Model is a more complex model than Model 2, and it includes more detailed representations of processes such as photosynthesis and respiration. The Bern Carbon Cycle Model is often used for research purposes.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Model 2, Model 2 the carbon cycle answer key
Model 2 is a valuable tool for understanding the carbon cycle, but it has some limitations.
- Strengths:
- Provides a simplified framework for understanding the dynamics of the carbon cycle.
- Can be used to predict future carbon dioxide levels.
- Can inform policy decisions related to climate change mitigation.
- Weaknesses:
- Assumes that the carbon cycle is a closed system, which is not entirely accurate.
- Does not include all of the processes that occur in the carbon cycle.
- Can be computationally expensive to run.
- Improved representation of processes: Model 2 could be improved by including more detailed representations of processes such as photosynthesis and respiration.
- Inclusion of additional compartments: Model 2 could be improved by including additional compartments, such as the cryosphere and the deep ocean.
- Improved data on carbon fluxes: Model 2 could be improved by using more accurate data on carbon fluxes.
Future Developments and Refinements
Model 2 is a continuously evolving model, and there are several areas where it could be improved.
FAQs: Model 2 The Carbon Cycle Answer Key
What are the key assumptions of Model 2 of the carbon cycle?
Model 2 assumes that the carbon cycle is in a steady state, meaning that the amount of carbon entering the system is equal to the amount leaving the system.
What are the limitations of Model 2 of the carbon cycle?
Model 2 does not account for the effects of human activities on the carbon cycle, such as the burning of fossil fuels.
How is Model 2 used to predict future carbon dioxide levels?
Model 2 can be used to predict future carbon dioxide levels by simulating the effects of different scenarios, such as changes in land use or energy consumption.