Delving into the intricacies of label the organelles in the composite cell, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative, with an authoritative tone that is both engaging and thought-provoking from the very first sentence. It establishes the significance of organelle labeling in composite cells, highlighting its role in advancing our understanding of cellular processes and paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in various scientific fields.
The content of the second paragraph provides descriptive and clear information about the topic, setting the stage for the subsequent sections that delve deeper into the types of organelles, labeling methods, advantages, limitations, and applications of organelle labeling in composite cells.
1. Introduction
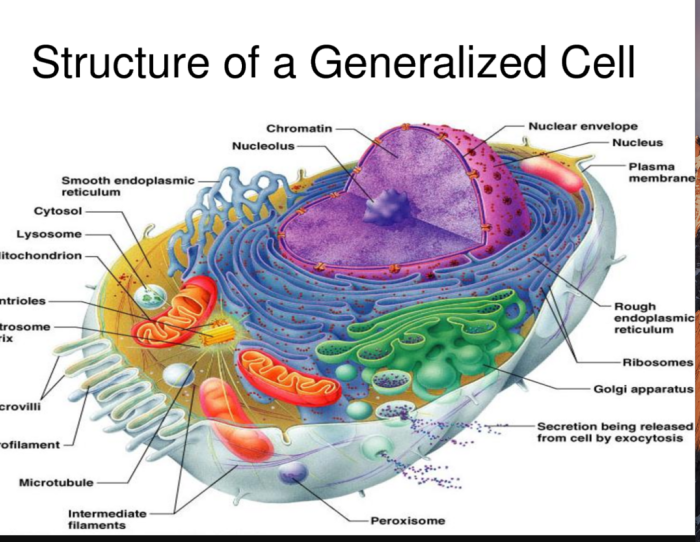
Organelles are specialized structures within cells that perform specific functions essential for cell survival and function. Labeling organelles in composite cells, which are artificial cells created by combining components from different cell types, allows researchers to visualize and study these structures in detail.
This technique has revolutionized cell biology, providing insights into cellular processes and advancing fields such as drug discovery and disease diagnosis.
2. Types of Organelles
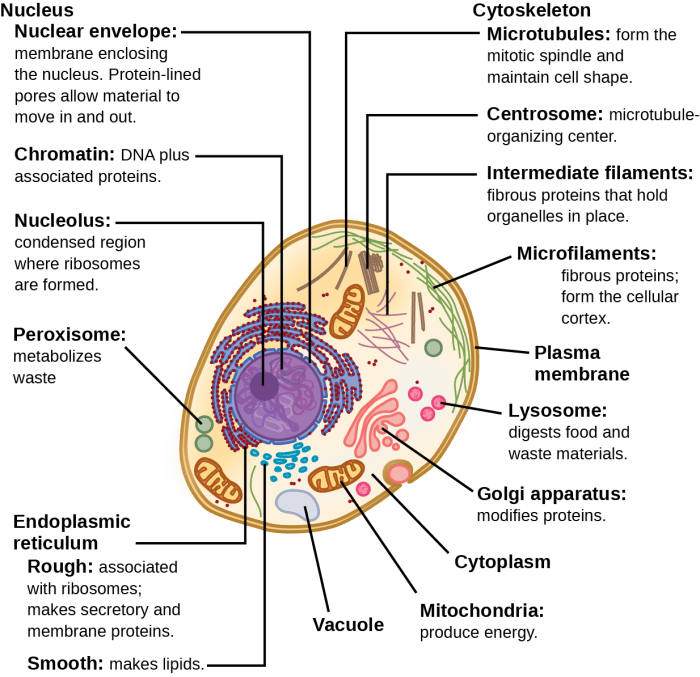
| Organelle | Function | Structure | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material (DNA) and controls cellular activities | Double-membrane bound, contains chromatin and nucleolus | [Optional: Image of nucleus] |
| Mitochondria | Produces energy (ATP) for the cell | Double-membrane bound, has inner folds (cristae) | [Optional: Image of mitochondria] |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Synthesizes and transports proteins and lipids | Network of interconnected membranes, can be rough (with ribosomes) or smooth | [Optional: Image of endoplasmic reticulum] |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids | Stack of flattened sacs (cisternae), surrounded by vesicles | [Optional: Image of Golgi apparatus] |
| Lysosomes | Digests and recycles cellular waste | Membrane-bound vesicles containing hydrolytic enzymes | [Optional: Image of lysosomes] |
| Vacuoles | Stores water, ions, and nutrients | Membrane-bound sacs, can be large or small | [Optional: Image of vacuoles] |
3. Methods for Labeling Organelles
Immunofluorescence: Uses antibodies conjugated to fluorescent dyes to bind to specific proteins within organelles.
Electron Microscopy: Uses electron beams to create high-resolution images of organelles, revealing their ultrastructure.
Fluorescent Dyes: Specific dyes can be used to stain organelles based on their chemical composition or function.
4. Advantages and Limitations of Labeling Organelles
Advantages, Label the organelles in the composite cell
- Improved visualization and identification of organelles
- Understanding of cellular processes and interactions
- Drug discovery and disease diagnosis
Limitations
- Potential artifacts or non-specific binding
- Interference with cellular function
- Limited resolution or sensitivity in some techniques
5. Applications of Organelle Labeling
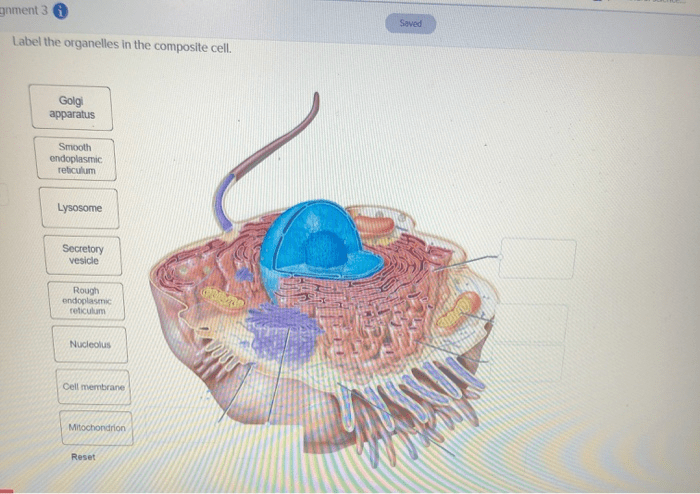
- Studying cellular metabolism and energy production
- Investigating protein synthesis and trafficking
- Developing drugs that target specific organelles
- Diagnosing diseases by identifying abnormal organelle function
Popular Questions: Label The Organelles In The Composite Cell
What are the key advantages of labeling organelles in composite cells?
Labeling organelles in composite cells offers several advantages, including enhanced visualization, improved identification, and a deeper understanding of cellular processes. It enables researchers to track organelle dynamics, study their interactions, and gain insights into their roles in maintaining cellular homeostasis and responding to various stimuli.
What are the limitations of organelle labeling techniques?
While organelle labeling techniques have revolutionized cell biology, they also have certain limitations. Potential artifacts, non-specific binding, and interference with cellular function are some of the challenges associated with labeling methods. Additionally, the choice of labeling technique depends on the specific organelle being targeted and the desired level of resolution.
How is organelle labeling applied in drug discovery and disease diagnosis?
Organelle labeling plays a crucial role in drug discovery and disease diagnosis. By selectively labeling specific organelles, researchers can investigate the effects of drug candidates on cellular components and identify potential therapeutic targets. In disease diagnosis, organelle labeling aids in the identification of cellular abnormalities associated with various pathological conditions, facilitating early detection and personalized treatment strategies.