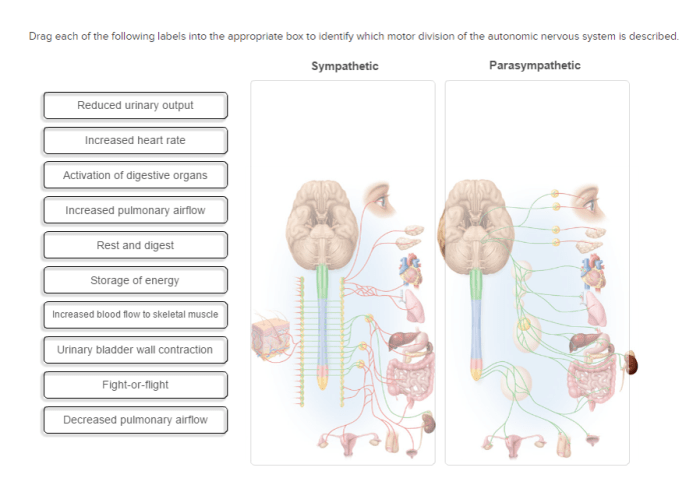
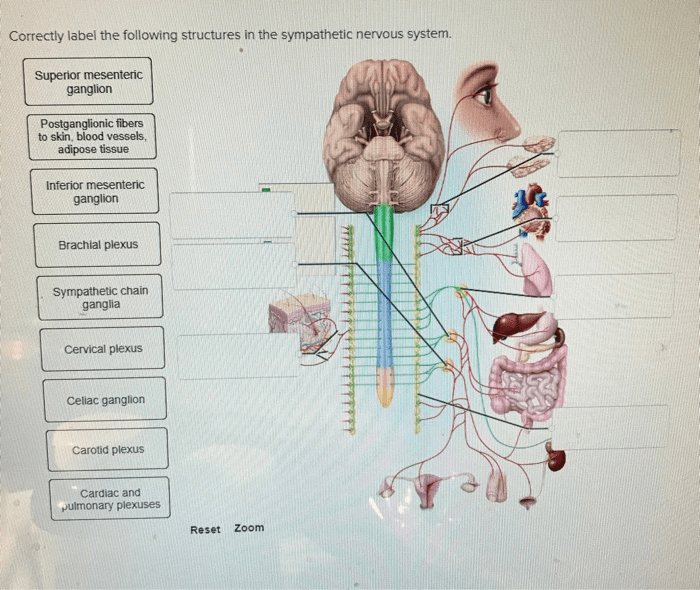
Correctly label the following structures in the sympathetic nervous system – Correctly labeling the structures of the sympathetic nervous system is crucial for understanding its anatomy and function. This intricate system plays a vital role in regulating various bodily processes, from heart rate to digestion. By understanding the location and function of its key components, we gain insights into the complex mechanisms that govern our physiological responses.
The sympathetic nervous system, a division of the autonomic nervous system, is responsible for the body’s “fight-or-flight” response. It prepares the body for physical exertion by increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, and redirecting blood flow to muscles. This system comprises several interconnected structures, including sympathetic chain ganglia, the sympathetic trunk, and prevertebral ganglia.
Define the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is a division of the autonomic nervous system responsible for regulating the body’s “fight-or-flight” response.
It is activated in situations of stress or danger, triggering a series of physiological changes that prepare the body to respond quickly and effectively.
Locate and Label Key Structures of the SNS
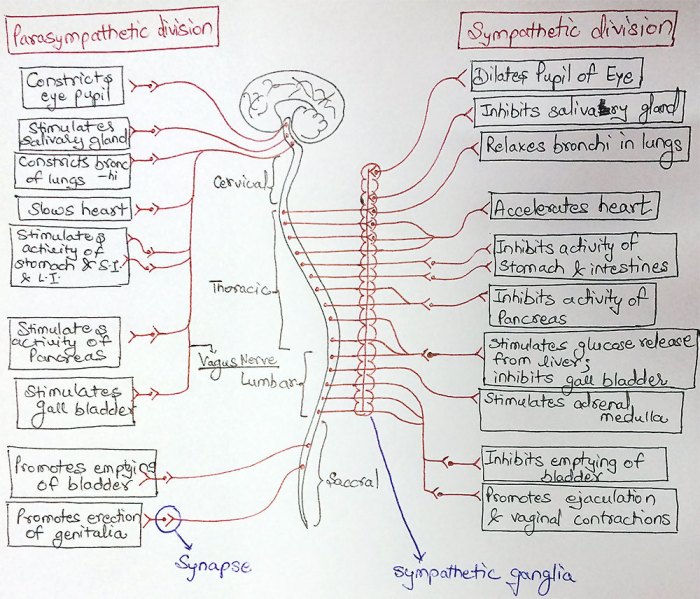
Sympathetic Chain Ganglia
The sympathetic chain ganglia are a series of interconnected ganglia located along the length of the spinal cord.
They receive input from the spinal cord and transmit impulses to the sympathetic prevertebral ganglia.
Sympathetic Trunk
The sympathetic trunk is a collection of nerve fibers that connect the sympathetic chain ganglia.
It runs alongside the spinal cord and transmits impulses from the ganglia to the prevertebral ganglia.
Sympathetic Prevertebral Ganglia
The sympathetic prevertebral ganglia are located in the abdomen and pelvis.
They receive impulses from the sympathetic trunk and distribute them to the target organs.
Trace the Pathway of Sympathetic Impulses
Sympathetic impulses originate in the spinal cord, specifically in the lateral horn of the thoracic and lumbar segments.
These impulses are transmitted through the sympathetic chain ganglia and then to the sympathetic prevertebral ganglia.
From the prevertebral ganglia, the impulses are distributed to the target organs.
Describe the Neurotransmitters Involved in the SNS
Primary Neurotransmitter
The primary neurotransmitter of the SNS is norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
Norepinephrine is synthesized in the sympathetic neurons and released upon stimulation.
Other Neurotransmitters
Other neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine and dopamine, can also modulate SNS activity.
For example, acetylcholine is involved in the parasympathetic response, while dopamine is involved in regulating blood pressure.
Provide Examples of Sympathetic Nervous System Functions: Correctly Label The Following Structures In The Sympathetic Nervous System
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Regulation
The SNS increases heart rate and blood pressure by stimulating the release of norepinephrine.
This causes the heart to beat faster and the blood vessels to constrict, increasing blood pressure.
Fight-or-Flight Response
The SNS is activated in response to stress or danger, triggering the “fight-or-flight” response.
This response involves a series of physiological changes, including increased heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration.
Other Functions, Correctly label the following structures in the sympathetic nervous system
The SNS also plays a role in other functions, such as pupil dilation, sweating, and digestion.
It helps to prepare the body for physical activity and to respond to environmental changes.
FAQ Guide
What is the function of the sympathetic chain ganglia?
The sympathetic chain ganglia are responsible for transmitting sympathetic impulses from the spinal cord to the target organs.
What is the role of the prevertebral ganglia?
The prevertebral ganglia distribute sympathetic impulses to the abdominal and pelvic organs.
What is the primary neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system?
The primary neurotransmitter of the sympathetic nervous system is norepinephrine.